We provide sustainable solutions that empower our customers to create a brighter future.
As our company continues to grow, we remain committed to developing solutions that enable our customers to deliver power more efficiently and sustainably. This commitment reflects our deep belief in environmental responsibility—a value we integrate into every facet of our operations, aligning our stakeholders with our core principles.
What is an Environmental Product Declaration?
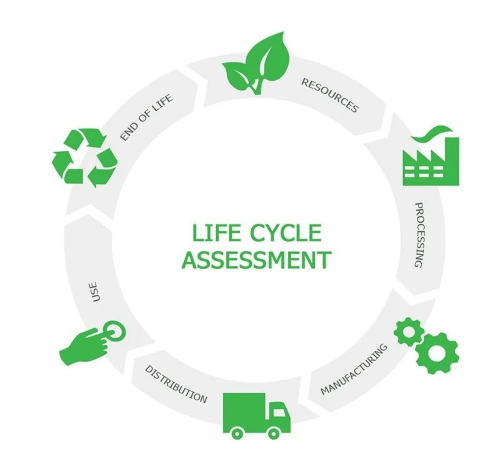
An Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) provides a clear and transparent report of verified, objective, and comparable data regarding the environmental performance of products and services throughout their entire life cycle. While the EPD serves as the final report, it is based on a foundation of life cycle assessment (LCA).
An LCA is a standardized method used to evaluate a product's environmental performance from a "Cradle-to-Grave" perspective. This approach considers the entire value chain, starting from raw material extraction, through manufacturing, to usage, and finally the product's end-of-life disposal.